The aging workforce is a key factor shaping the future of work. In most major economies today, there are around six workers for every retiree. By 2030, all Baby Boomers will have reached 65, the general retirement age threshold, meaning this figure is set to drop substantially.
As Boomers leave the workforce, employers are trying to stem the bleeding from the skills, knowledge, and experience they’ll take with them by finding ways to keep them on the payroll. Organisations that recognise the value of older workers can benefit from leveraging this talent pool. Here, we explore four strategies to help you retain older workers or entice them to return.
Who are the Baby Boomers?
First, let’s take a closer look at the demographic. Baby Boomers are individuals born between 1946 and 1964, the largest generation in history. This generation was born following World War II and lived through the Civil Rights Movement, the Cold War, and massive technological advancements. They are a major force in the global economy and have built and defined the labour market we know today.
Boomers are the most affluent generation in history, and they are expected to pass on trillions of dollars to their children and grandchildren, which could reduce the labour participation of younger generations. Combined with today’s decreased birthrates, the global workforce is already shrinking as Boomers increasingly retire.
A Global Look at Retirement
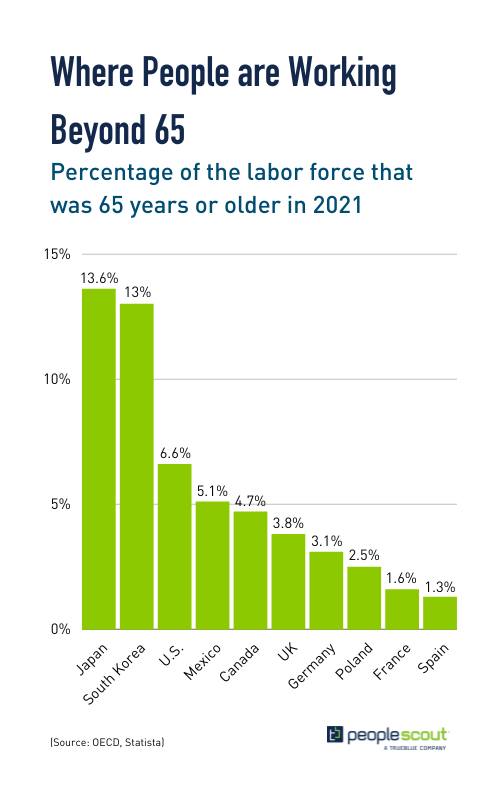
According to Pew Research Centre, approximately 2 million Baby Boomers retire every year. In 2020, this number swelled to a historic high as 3 million workers retired from the workforce in the U.S. alone.
However, attitudes toward retirement vary widely across countries and are influenced by both culture and economics. For example, in the United States, where people value individualism and self-reliance, retirement is seen as a time to relax and enjoy life. But in Japan, there is a strong emphasis on collectivism and community, which can lead people to feel they should continue working and contributing to their circle.
Despite people working longer in Japan, the country is projected to have a ratio of just 1.5 workers per retiree at the start of the next decade. In some of Europe’s biggest economies and the U.S., the outlook is not much better with figures hovering around the 2.4 mark. This is due to declining global birthrates, which has fallen by half since 1950. In short, there aren’t enough Millennials and Gen Z-ers to fill Boomers’ shoes.
The exodus of Boomers from the workforce is having a significant impact on the global economy, and some countries are beginning to raise the retirement age to push back the impending dropoff. Moreover, in recent months, as the cost of living has gone up, there’s been a surge in “unretirement” as some who left work during the pandemic are looking for jobs again.
Boomeranging Boomers: Why are Retirees Coming Back to Work?
In the UK, the number of people over 65 working or looking for work hit nearly 1.5 million in the second half of 2022—the highest level on record per the ONS. According to a recent report from Paychex, one in six retirees are considering returning to work.
Some common reasons for coming out of retirement cited in the report include:
- Financial need. For some retirees, savings and pensions may not be enough to cover expenses, especially if they accrue medical bills. Over half (55%) of retirees who have returned to work say they needed more money. Going back to work, even part-time, can make a difference in their financial situation.
- Lack of purpose. Jobs create structure and routine in an employee’s life. Losing this can be a difficult adjustment for some after retirement. Some may also feel they are no longer contributing to society or making a difference; returning to work can give these individuals a sense of purpose and fulfillment.
- Socialisation. Work provides a social outlet. In fact, 43% of retirees say feeling lonely is a motivator for returning to the workforce. Work creates opportunities to socialise as employees interact with co-workers and customers.
- Boredom. Work can provide mental and physical stimulation for retirees. Boredom is cited as a reason for returning to work for 52% of survey respondents. Working can help older people stay sharp and active.
- Enjoyment of work. Some retirees simply enjoy working. They may find their jobs to be challenging and rewarding, and they may not be ready to give them up when they reach retirement age.

Attracting & Retaining Older Workers
While older people may be keen to return to the workforce, the job they want in the latter part of their life won’t look like their previous career. They may seek to change how, when, and where they work—including moving to part-time positions or changing fields or job roles. If employers make certain concessions, Baby Boomers might be persuaded to stay a little longer, therefore preventing the “cliff-edge” effect.
So, how can you retain the older workers you have for a little longer or entice them back? Here are four things to consider.
1. Address Ageism in the Workplace
The majority (73%) of those in their 50s and 60s feel they share invaluable skills, experience, and knowledge with colleagues—but 16% believe it is not valued by their employer. Indeed, 62% of hiring managers admit they “are skeptical about hiring retirees.” It’s no wonder that 74% of working retirees “feel judged by co-workers because of their age.”
Creating a sense of inclusion and belonging is crucial for both attracting and retaining older workers. If you have a diversity training program in place, ensure that ageism is being addressed in your training materials. If you don’t have a training program, consider creating one. Not only will you see an improved business performance, benefiting your bottom line, but your employees of all ages will be more engaged, content and productive.
2. Add More Flexible Working Arrangements
Boomers may continue to work after retirement age, but that doesn’t mean they’re seeking the same kind of career. Few of this generation will want to continue working in a typical full-time contract after they hit 65. Family responsibilities and the desire for more leisure time are key concerns for them. Many won’t want to continue taking on high-pressure responsibilities either.
Flexibility and work/life balance are important across all age groups, with Millennials, Gen X and Baby Boomers rating it as a top consideration when looking for a job in a recent survey. Amongst retirees looking to return to work, 53% want a remote position according to the Paychex survey.
3. Provide Training & Mentoring
Older employees, especially those who have returned to the labour force from retirement, value opportunities to learn and develop new skills. Organisations that provide chances for older workers to expand their knowledge and skills have a stronger chance of retaining this talent pool. This could include things like offering new technology training or mentoring or coaching opportunities.
Reverse-mentoring programs have become a popular way to engage both older workers and younger employees who are hoping to build leadership skills. Unlike a typical mentorship, reverse-mentoring involves a younger employee mentoring an older, more experienced mentor. Not only can this help older workers develop digital skills, but it also contributes to a culture of inclusion.
4. Create Opportunities for Knowledge Transfer
While it’s important that older workers harness new skills, it’s equally crucial to ensure that skills aren’t lost from generation to generation. There is already a skills shortage in many fields, from haulage to engineering and healthcare to hospitality. Losing the Boomer demographic from the workforce will intensify the challenge of filling skilled roles—not to mention reduce the dissemination of knowledge for the generations that follow.
The biggest responsibility for Baby Boomers is knowledge transfer and mentoring. Organisations must create opportunities for more experienced employees to work closely with new joiners and less experienced colleagues to impart their wisdom and share their organisational and sector connections. This way organisations can ensure these skills, insights, and knowledge are not lost and can be leveraged for years to come.
Embracing the Aging Workforce
In this tight labour market, employers need to keep an eye out for opportunities to capitalise on the experience and knowledge that older workers possess, particularly as they withdraw from the labour market. Baby Boomers offer loyalty, passion, and confidence. Embracing the aging workforce could prove to be a lifeline for organisations that are planning for a future labour shortage.
Check Out Our Report To Learn More About The Future Of Work