Around 3,547,000 people between the ages of 50 and 64 are currently economically inactive, or not working, making older workers one of the most in-demand talent pools for employers today. It’s crucial for retail and hospitality employers to know how to entice older workers back to work and to make the most of their valuable talent.
In the UK, the government launched a ‘returnership’ initiative to inspire those over the age of 50 to come back to work or to seek a career change. This scheme involves three programmes that help older workers retrain and learn new skills, providing workers with a clear roadmap back into the workplace and encouraging organisations to hire them.
Known as the ‘sandwich generation’—defined by caring for their elderly parents and also dependent children or grandchildren—these older works have a strong work ethic. Customer facing and front of house roles enable them to fit work around caring for family and other responsibilities.
Our recent webinar with Personnel Today featured a panel of HR and talent acquisition experts discussing the wants and needs of older workers and how best to utilise this talent pool’s experience. Keep reading for key insights from our panel discussion and get the latest research to understand exactly what older workers want and what retail and hospitality organisations can do attract this in-demand demographic.
What Do Older Workers Want?
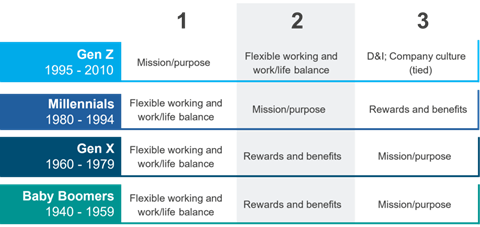
What do over 50s want and need from an employer? Does your organisation know how to attract and engage this older workforce and how to hire and retain them?
Flexibility
Unsurprisingly, monetary concerns are coaxing older workers back into the workplace due to the cost-of-living crisis. However, when it comes to choosing an employer, flexibility takes precedence over money.
Hospitality roles typically attract a younger demographic of workers. However, the flexibility offered by these jobs also appeals to the older working generation. Given that the over 50s are the largest age group with caring roles, flexible and part-time work is a powerful motivator for them to fit a job into their routine.
As well as permanent roles, seasonal and flexible roles are available within the hospitality and retail industries, which can be more attractive to the older working community. Working harder in those seasonal months creates work-life balance, allowing older workers to take time off during quieter periods to recover and be with their friends and family.
Sense of Belonging
Workers in this age rage are still searching for rewarding work. Older workers wish to find a place where they can feel a part of their local community and give back. Over 50s enjoy creating social connections that a customer-facing job in a restaurant or supermarket can provide.
Customer-facing roles in hospitality and retail give individuals the chance to serve and connect with their community. For older customers, seeing employees in shops and restaurants that represent them can boost the customer experience.
Myths About Older Workers
There are plenty of misconceptions out there from employers and colleagues about hiring and working with older workers. Consider these myths busted.
Myth 1: Older Workers are Resistant to Technology
Certain words can be viewed as a turn off for an over 50s audience, including “tech-savvy”, which some see as a way to ward off older candidates. There are older people who will feel excluded because others wrongly perceive that they’re less capable with technology, when in fact they are part of a generation that has seen huge advancements in technology. Bill Gates, the co-founder of Microsoft, is in his late 60s, and Tim Cook, the CEO of Apple is in his early 60s.
Recognise that all colleagues work differently with technology, so you must be thoughtful in your use of training. In hospitality and retail, workers are likely to be using tills and sales computer systems. Regardless of whether a person struggles with technology, an organisation should have a strong programme in place to support workers as they learn how to use these tools. For example, consider implementing a buddy system of workers and leaders who will happily help new employees in their first few weeks as they learn point-of-sale systems.
Myth 2: Absences are Higher Because of Health Issues
As people get older, their health can decline. However, this doesn’t mean that absenteeism is higher amongst older workers. In fact, older workers are more likely to have higher everyday attendance rates due to their strong work ethic. When you do see sickness or absence, it is typically in the form of long-term leave, rather than the odd day here and there.
Myth 3: Older Workers are Less Productive Than Younger Workers
A study demonstrated that there was no different between younger and older workers in terms of productivity. This study found that with their years of experience and memories, older people perhaps dismiss new information when they process things and instead use past information. It’s therefore important to acknowledge that older workers aren’t doing things worse, they just do these things differently through their years of experience.
What Can Organisations Do to Attract Older Workers?
So, how can retail and hospitality organisation tap into this hard-working talent pool? Here are four questions to ask to ensure your talent acquisition programme is over-50s friendly.
Are Your Candidate Attraction Materials Inclusive for Everyone?
To attract older workers, you must think more creatively and broadly. Use community-based websites to engage with people who live close to your locations. Show how the job will fit into their lifestyle and what it would be like for an older person to work there, rather than a generic message. Create testimonials from your current employees to support this.
Make sure that your imagery is diverse, featuring people of all ages. Look at your marketing materials and ensure that it reflects the community so that over 50s can see that jobs in hospitality are here for them. Take advantage of local community-boards in village halls and supermarkets.
How is Your Candidate Experience?
Retention and attraction are very different. Employers can encourage people to apply for jobs through their advertisements, yet ultimately, it is down to the experience the candidate has during the recruitment process, induction and beyond. The candidate experience is what will make them accept the position and stay at the company.
When younger workers leave education, they’re taught how to answer competency-based interview questions and how to write a CV. The older generation of workers likely won’t have a CV and may not have experience with this kind of interview. Is your interview process age inclusive and relevant to them?
Are You Giving Them What They Want?
Now that we’ve shared what older workers want, is your organisation serious about flexible shift patterns? Over 40% of the part-time workforce is aged over 50. Not only does this part-time schedule work in hospitality, but also in retail, in which the holiday season creates a huge demand for workers.
Different shift patterns in retail can support individuals in their family commitments and lifestyle. Look at your employees’ caring responsibilities, for partners, for children, for elderly parents, and take this into account when creating your shift offerings.
But what else does this generation want from you? Everyone responds well to positive feedback. Both the retail and hospitality industries are great at celebrating successes, shown through brilliant behaviour and examples across organisations.
Finally, show that your organisation values them by offering benefit packages. Health is a priority for everyone as we get older, and health benefits can help to attract them to your organisation.
Does Your Anti-Bias Training Include Age?
Ageism usually gets the least amount of focus across the DE&I plan. Train your leaders and hiring managers on unconscious bias particularly as it relates to age. Ensure there are no biases lurking in the recruitment process to open up talent pools instead of closing them down.
Interested in learning more about engaging and attracting older workers directly from HR and talent acquisition professionals? Check out our on-demand webinar recording with Personnel Today and a panel of experts from Tesco, Fuller’s, Rest Less and Bourne Leisure.